Import relational data into Neo4j using Apache Hop with our dedicated Neo4j Output guide. Enhance...
Importing Relational Data to Neo4j using Apache Hop - Graph Output
Effortlessly import relational data to Neo4j using Apache Hop. Transform your data with the Graph Output plugin.
Introduction
Hello and welcome to this tutorial on how to import relational data into a Neo4j database using Apache Hop.
If you are here I suppose you already know about Neo4j and Apache Hop, let’s say that having a basic understanding of the property graph model is the only requirement to have the task done.
The idea is exporting data from a relational database system (we’ll use PostgreSQL in this case) and importing the data into a Neo4j database (graph database) using the Neo4j Graph Output transform (Apache Hop plugin).
You can find the code and the files in the public repo how-to-apache-hop.
We can divide the task into small pieces:
- First, we need to translate the relational schema to a graph model.
- Then, we configure or design the translation in Apache Hop. We create a graph model metadata object in Apache Hop.
- Finally, we implement a pipeline in Apache Hop to extract the data from the relational database and loading the data to the Neo4j database.
You can also check our post Apache Hop: Importing relational data into Neo4j - Neo4j Output, which is similar but in that case we load all the nodes, not only the nodes with at least a relationship and we use another Apache Hop plugin: Neo4j Output.
The relational database
We are going to use a sample PostgreSQL database. The dvdrental database represents the business processes of a DVD rental store, including data about the films, actors, and demographic data of the staff.
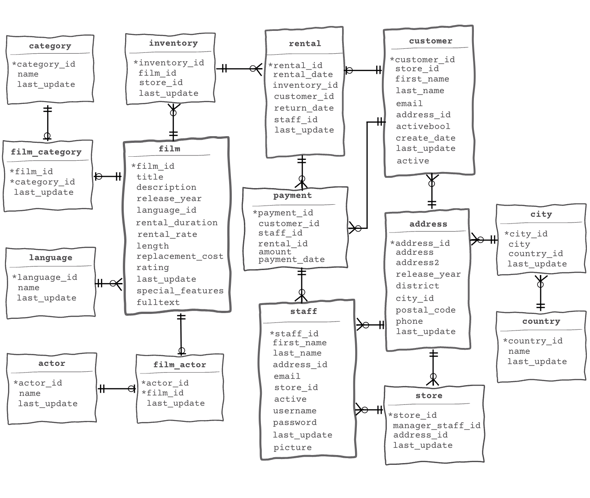
🗒 To keep the graph smaller, we just choose some of the entities that are most relevant for our graph and would most likely benefit from understanding the relationships in our example.

Step 1: Translate the relacional schema to the graph schema
Based on this, we convert our relational model to a graph model.
Nodes and Labels
-
Each row on our Actor table becomes a node in our graph with Actor as the label.
-
Each row on our Film table becomes a node with Film as the label.
-
Each row on our Category table becomes a node with Category as the label.
-
Each row on our Language table becomes a node with Language as the label.
Relationships
-
The join between Actor and Film becomes a relationship named ACTS_IN.
-
The join between Film and Category becomes a relationship named BELONGS_TO.
-
The join between Film and Language becomes a relationship named IN.
If we draw our translation on a whiteboard, we have this graph data model.

Step 2: Create the graph model in Apache Hop
You can build a Neo4j Graph Model in Apache Hop as a metadata object. A graph model in Apache Hop allows you to create nodes with their attributes, as well as the connections between these nodes.
The Neo4j Graph Output transform's input fields may then be mapped to properties using a graph model.
The following is how the dvdrental graph model is set up.
Model tab

Model name: set the name of the graph model (dvdrental).
Nodes tab

- Name: specify the node name (Actor).
- Labels: choose the label name (Actor).
- Properties: set the property keys (actor_id, last_name, first_name) and the property types (Integer, String, String).
- Primary: specify the primary key (actor_id).
As we did for the node Actor, configure an entrance for the rest of the nodes: Film, Category and Language.
Relationships tab

Configure all the relationships by specifying the fields:
-
Name: specify the name of the relationship (ACTS_IN).
-
Label: set the name of the label for the relationship (ACTS_IN).
- Source: specify the origin node of the relationship (Actor).
- Target: specify the target node of the relationship (Film).
As we did for the relationship ACTS_IN, configure an entrance for the rest of the relationships: BELONGS_TO and IN.
Graph tab
You can visually check the model you just created.

The data may now be imported into the Neo4j database. Using a Table Input and a Neo4j Graph Output transform, we build an Apache Hop pipeline:

SQL query
SELECT a.actor_id,
a.first_name,
a.last_name,
f.film_id,
f.title,
f.description,
f.rental_rate,
c.category_id,
c.name as category,
l.language_id,
l.name as language
FROM public.actor a
JOIN film_actor fa ON fa.actor_id = a.actor_id
JOIN film f ON f.film_id = fa.film_id
JOIN film_category fc ON fc.film_id = f.film_id
JOIN category c ON c.category_id = fc.category_id
JOIN language l ON l.language_id=f.language_id;


- Transform name: choose a name for this transform in the pipeline (write-graph).
-
Neo4j Connection: select the Neo4j connection to write the graph to (neo4j-connection).
-
Graph model: select the graph model we created (dvdrental).
-
Fields: to map the input-output fields, you can use the Map fields option.
We just have to map the concepts following the same rules.

You can select the fields and hit the Add option or use the Guess option to generate all the mappings.
The mapping looks like this in the image:

Now you’re ready to run the pipeline:

The dvdrental knowledge graph
If your pipeline runs successfully, you will get a graph database containing your dvdrental data.
Let's explore the graph database you just loaded.
Cypher
CALL db.schema.visualization;

Run the following Cypher code to see some of the nodes:
Cypher
MATCH (n) RETURN n LIMIT 15;





.png?height=200&name=Featured%20images%20(7).png)
-2.png?height=200&name=Featured%20images%20(3)-2.png)
